The magnitude of problems
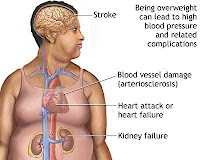
Obesity is not just a social problem. It is a DISEASE of epidemic propotions. A large number of systemic diseases are associated with it. Diabetes, hypertension, cardiac problems COPD and obstructive sleep apnea are the common problems. In addition the bones and joints are unable to support the weight for a long time causing osteoarthritis. This in turn leads to decreased mobility which further increases the weight and a viscious cycle ensues. The leading killer in the obesity patient is the heart attack. On an average obesity decreases ones life span by 6-10 years when BMI is more than 35. Other associated diseases are stroke, psychiatric illness, Infertility, menstrual irregularity, deep vein thrombosis... and the list goes on. In short ones physical and psychological well being is affected by obesity.
 Many factors play a role in development of obesity. Genetic predisposition plays a major role. All persons on a same diet have different gain in weight. You would have noticed that some eat very little but put on weight quickly. Another case is hormonal dysfunction. Both these factors are beyond our control. However, there are certain factors which we can control.
Many factors play a role in development of obesity. Genetic predisposition plays a major role. All persons on a same diet have different gain in weight. You would have noticed that some eat very little but put on weight quickly. Another case is hormonal dysfunction. Both these factors are beyond our control. However, there are certain factors which we can control.- Diet - The change in our food habits and the easy accessibility to junk food has played a major role in this epidemic. Our children now eat foods with high carbohydrate and oil content. The excessive calorie intake from early age has played a major role in certain cases.
- Sedentary lifestyle - All over the world there is a shift to less physically demanding works. About 30-50% of the world population has insufficient exercise. The introduction of television has played a major role in childhood obesity .
In India obesity now of epidemic pro-potions affecting 5 % of the population. Kerala now has the dubious distinction of being burdened with 24% of males and 34% of all females being overweight.
ARE YOU OBESE ?
Obesity is calculated by body mass index ( BMI) which is calculated as BMI= Height (cm) / (weight kg)2
BMI
|
Classification
|
<18.5
|
Underweight
|
18.5-24.9
|
Normal
|
25-29.9
|
Overweight
|
30-34.9
|
Obese
|
35-39.9
|
Severe obesity
|
>40
|
Morbid obesity
|
>50
|
Super obesity
|
In India as we are a population with high incidence of metabolic syndrome ( diabetes, hypertension, Cardiac problems etc. ). It is appropriate to bring down the upper limit of the normal BMI to 23.
It is easy to tell an obese person to eat less but the reality is not so simple. In fact many obese persons eat much less than the average normal individual. Most of them have an inherent ability to absorb more and store energy as fat that works against them. The aim of the treatment is to achieve a healthy weight than the ideal weight Treatment can be medical or surgical
Medical : 1. Dietary changes
2. Exercise
3. Weight loss medications
Diet : Avoid fasting but change your diet. They usually don’t work in the long term if your BMI is too high due to a condition called as yoyo syndrome ( with every cycle of weight loss followed by weight gain your weight actually increases a few kilos than what it was previously ). Eat a low calorie diet, less of carbohydrates like rice and more of vegetables and fruits. Avoid high calorie junk foods, egg wheat and fish are high in proteins and low in fat .
Exercise : Increase your daily exercise. Use steps instead of the lifts wherever possible. Walk when you can avoid using a vehicle. Exercise with a trainer or at a gym for atleast 250- 300 mts a week. A change in general attitude is required. The motivation to loose weight is most important for a long term sustained weight loss.
Drugs - Orlistat : Used in adults and children more than 12 years . This blocks fat absorption from the intestine and reduce weight in the long term. Other drugs might have minimal effects, but may not be useful in the long term.
Weight Loss Surgery - Bariatric Surgery : These are recommended in persons with BMI > 40 or BMI>35 if having comorbidities like diabetes or hypertension. These persons should have undergone trials with dieting and exercise before opting for surgery .
There are two types –
1. Restrictive procedures
2. Malabsorptive procedures .
These surgeries work by restricting the amount of food that can be taken hence reducing the calorie intake. The most common of the procedures done are the Sleeve Gastrectomy and Lap Banding. Sleeve gastrectomy has an additional benefit of taking away the part of the stomach which is responsible for increased appetite hence increases satiety and reduces intake.
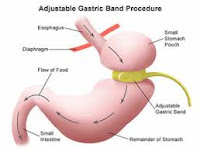 These procedures require a support from the patient because if the person keeps eating food which is high in calorie but low in bulk ( like sweet eaters ), they tend to fail to loose weight. The persons generally tend to loose upto 80% of their excess body weight over a period of few months .
These procedures require a support from the patient because if the person keeps eating food which is high in calorie but low in bulk ( like sweet eaters ), they tend to fail to loose weight. The persons generally tend to loose upto 80% of their excess body weight over a period of few months .Malabsorptive surgeries :
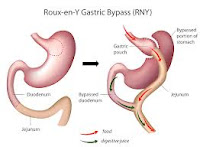 These surgeries effectively divert the food from a major portion of the intestine, thereby effectively reducing the calorie absorbed and hence reducing weight. The surgeries include Roux En Y Gastric Bypass Surgery (the gold standard) and DJ Bypass with duodenal switch. These procedures are the most effective but have higher complications.
These surgeries effectively divert the food from a major portion of the intestine, thereby effectively reducing the calorie absorbed and hence reducing weight. The surgeries include Roux En Y Gastric Bypass Surgery (the gold standard) and DJ Bypass with duodenal switch. These procedures are the most effective but have higher complications.OTHER BENEFITS OF SURGERIES :
Diabetes Mellitus : DM is completely resolved or reduced to a much manageable levels following the surgery in about 80-95% of the case. This is surprisingly not related to the reduction in weight as the normalization of the sugar levels are seen soon after surgery in many cases.
Hypertension : This is cured in 75-90% of the cases.
Menstrual irregularity, Infertility and arthritis are also resolved in many cases following surgery.
Surgery for Diabetes Mellitus :Today a new trend for surgery for diabetes has come. This was due to the dramatic improvement in the diabetes status which was noted in the cases which underwent bariatric ( weight loss ) surgery as mentioned above. The same has been applied to case with normal BMI people with diabetes with promising results but is still not recommended outside of clinical trials .
The treatment of obesity has progressed in leaps and bounds in the last 10 years. The surgeries for weight loss have been researched extensively to validate its safety and has reached a stage where it is predictable as well as safe with minimal complications. All persons with BMI > 40 or with BMI more than 35 with diabetes or hypertension should be considered for these procedures if the conservative approaches fail.
About MIMS Hospital:
About MIMS Hospital:
The Malabar institute of Medical sciences Ltd (MIMS), the first NABH Accredited multispecialty Hospital in India, is situated in the heart of Calicut (Kozhikode), Kerala, India. It is a pioneer hospital in India renowned for its excellent medical expertise, nursing care and quality of diagnostic services. For more details : Visit http://www.mimsindia.com
For other Articles Visit:
For other Articles Visit:





.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

















.jpg)
